Be yourself; Everyone else is already taken.
— Oscar Wilde.
This is the first post on my new blog. I’m just getting this new blog going, so stay tuned for more. Subscribe below to get notified when I post new updates.
Be yourself; Everyone else is already taken.
— Oscar Wilde.
This is the first post on my new blog. I’m just getting this new blog going, so stay tuned for more. Subscribe below to get notified when I post new updates.
Polymorphism is one of the many compounds words used in tech. Polymorphism could be translate as “many forms “. In Java polymorphism is the principle of adapting many form which means that allow you to use resources from other classes without needing to know which class is using it. An example of polymorphism are override and overload.
Now let’s talk about Overridden methods, usually utilizes the @Override annotation in tops of its method. This methods are run time examples of polymorphism. To override a method first we need to use another object oriented principles in this case would be inheritance because we need to bring methods that are in another class or interfaces and change its behaviors.
Unlike Overridden methods, Overloaded methods doesn’t provide annotation. We could say that this methods are more useful than overridden ones, but each of them serve its purpose. Overloaded methods are compiler time examples of polymorphism and they can be re-structure , you can either change its behaviors, the return type or the quantity of parameters.
An brief example of how they are used:
public class Animal {
public void sound() {
System.out.println("sound");
}
}
public class Cat extends Animal{
@Override
public void sound() {
System.out.println("miaw miaw ");
}
public void sound(int quantity, int age) {
System.out.println("miaws miaws");
}
}
public class Dog extends Animal{
@Override
public void sound() {
System.out.println("waof waof");
}
}
public class Shelter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat cat = new Cat();
dog.sound();
cat.sound();
cat.sound(1,3);
}
}
You have a class named “Animal” and you will have a class named “Cat” that will extends Animal because all cats are animals, You can override the method “sound” from “Animal ” class since each animal have different sound then create an instance in the main class to execute the methods and see what will do.
Some people may think about data structure as the one of the hardest part in Computer Science but to be honest it is not hard at all, I know it can get kind of complicated but when you read about or imagine in real life example you will feel more familiarized with it.
I know you hear about queues but what is a queue in programming? Queue is a collection that is use to hold elements and provide various operations (methods ) that we will discuss later on, as in real life queue follows the same principle like when you go to a cashier it is called FIFO and stands for First-In-First-Out.
Java already provide an interface that allow you uses its operation but today we are going to discuss and figure out how it works.
First imagine queue as the picture below:

One of the most important method for queue is the insert () method, this method as it will increase the size of the queue by adding elements to it.
Also we have the method remove() which decreases the size of the queue by removing the first element that was added .
Another cool method is Peek() method,

peek() method is the one in charge of returning the element that is in front position of the queue
When we have a fixed size collection as array we have to make sure we don’t over populate it because it will give us indexOutBound error and we don’t want it, that ‘s why invoke isFull() method which return a boolean value as true if the queue is full or false if not full.
Another method that return a boolean is isEmpty(), which follows the same logic and returning true whether is empty or false if not.
Just in case we encounter and indexOutBound exception and we want to keep using the same queue or we are only using arrays as a collection we can go for a circular queue which one it reaches it maximum size value, the next value after that will overwrite the first value and so on, And example of circular queue is this.
As conclusion queue are very important in such our daily basis when we are buying stuff and waiting in a line to pay or as in programming where we are hold the data or ordered line of clients. If you want to know more about it implementations or about other data structures you can click here.
As a transport layer the most common used is TCP which stands for Transmission Control Protocol. TCP make sure that the data sent by an application at one end of the internet is delivered in the order to the application at the end of internet , basically organize the data to send more reliable some applications most of the application that are web-client or email-client used it because its reliability but when an application don’t need it go for the other option which is UDP
UDP stands for User Datagram Protocol and it is used when an application doesn’t need that much reliable delivery that’s why some refer to it as “Unreliable datagram protocol.

Difference Between TCP and UDP
TCP :
UDP:

An application has the choice of at least two different Transport Layer services: TCP and UDP. You are the ones who decides what kind of protocols you will use for it and what it most convenient fortunately we have more than one option to pick.
I know sometimes JavaScript can be confused with Java because of the name or for its similarity with the syntax but definatively data type is one of the javaScript properties that differ from Java.
JavaScript variables can hold many types: objects, Strings , numbers, boolean and so on, this concept it is very important in programming because made the execution categorized and organized to follow.
Numbers: is a data type in java that consisting as its name says it in numbers in java and other languages we have data types like integers or float or doubles, but in java all falls in that category example:
var x = 16; // this is a number
var y = 16.586934 ; //this is a number tooString: This data have a rule, its value always have to be surround by quotes, a string is also known as array of characters group together example:
let str = "Hello World"; // this a string
let str = "number: 123"; // this also is a stringObjects: This is a special case because objects main role is to store collection of data basically you can store more than one type inside it example an Array is an object, which can contain many data types inside example:
let cars = ["Saasb", false, 2345,]; // this is an object
let person = {firstName:"John", lastName:"Doe", age:50}; // this is also an objectBoolean: This is a logical data type and only has two values “true” and “false” example:
let isMarried = true; // this is a boolean
let isOn = false; // this is a boolean
let isGreater = 50 > 45; // this will return true , which is also a booleanNull: This is also another special case , because the null value basically mean “nothing” it is use to clean other types example:
let age = 2019 - 1990;
age = null; // we are setting the age to null in a way to clean it
Undefined: Another case like “null” undefined values is given to a variable that has not value assigned example:
let age; // this will print out undefined because has not value assignedJust case you are not sure or don’t know what data type or what category falls a data type in javaScript, there is a method for you this method is called typeOf example:
typeof( 0); // "number"
typeof( true); // "boolean"
typeof( "foo"); // "string"
typeof undefined // "undefined"
This is a very helpful tool in JavaScript when we are trying to differ numbers from string and want to categorize it but it is also good to know the data types and what values they can hold.
For newbies in the web this maybe something weird to hear but HTML,CSS and JavaScript are the soul of the web, they are the languages that run it. (HTML) stands for Hypertext Markup Language , (CSS) Cascading Style Sheets and JavaScript.
They are very related to each others but designed to different task like siblings or brothers cleaning a house. HTML is adding meaning to raw content ,CSS is for formating that market up content basically it is the make up for html, the style or what make it loops pretty when its displayed and JavaScript is for make it more dynamic and interactive .
An example of HTML syntax is :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a Heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>To check it out we save the file as .html and run it in any browser , I highly recommend Chrome or Mozilla Firefox. The output will be this:

CSS and JavaScript can be added in different way to HTML it could be ether inside the HTML wrapped up by <Style> for CSS , <Script> for javaScript or creating a file and link it using reference link to the path for example:


An example of CSS syntax is :
body {
background-color: lightblue;
}
h1 {
color: white;
text-align: center;
}
p {
font-family: verdana;
font-size: 20px;
}
When we are saving it in a file we have to add the type .css at the end or it wont run also when we link it have to be inside head tag in html.
javaScript is one of the most famous programming language it provides a lot of functionality also it could be tedious because it doesn’t provide an actual IDE like others programming languages. Its functionality is mainly based to add interactive features to the HTML An example of this is :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>My First Web Page</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
<script>
document.write(5 + 6);
</script>
</body>
</html>
As we see in the example below inside the script we called a function to make a math operation and the rendered to the HTML, this is just a simple example of how manageable could be javaScript it can even manipulate HTML or CSS. The difference between all three is very obvious but each of them come taken by the hand of each other, and learning just this is the beginning of any web developer. You can have more information about them here.
You add a new meaning of a text when you surround it by a tag. Whenever you surround content in a <ul> or <ol> you are telling the browser that piece of text should be rendered as an unordered list ,<ul> or ordered list , <ul> to add individual values we use <li> as list.
An example of unordered lists is :
<h2>Lists</h2>
<p>Unordered list:</p>
<ul>
<li>ul: means unordered list and have to wrap the whole list</li>
<li>inside unorderedlist should be li, list elements</li>
<li>since is an unorderedlist they doesn't have order</li>
</ul>As the example below unordered list have a strict rule it have to be called with the <ul> tag and should only contain <li> elements.
An example of ordered list is:
<p>Ordered list:</p>
<ol>
<li>ol: means ordered list and have to wrap the whole lists</li>
<li>As we know li stands for list and goes inside </li>
<li>This list goes in incrementing order</li>
</ol>As we see in the example below ordered list have have a particular difference from unordered list as its name say ordered list have an order and this order is incrementing according to how many list you add.
This kind of list it is well use when we are using step-by-step procedures like instructions or recipes or topics that goes inside a field.
This is the third part of the design pattern chapter in this part we are going to talk about some behavioral patterns:
Command Design Pattern: You use an interface to call an execute command and based on which class is calling it, the command it runs will be different.

This design consist in an object wich is used to represent and encapsulate all the information to being use later for example in the UML above the execuse is called in differents object. you can see this video to give you throgh the implementation
Iterator Design Pattern: It is a way to access through different collections regardless of their type.
Observer Design Pattern: This behavioral pattern uses an object that notifies any subscribers on trigger of a certain event.

In other words this design patterns create an update to notify, you can see its implementation in this video
Strategy Design Pattern: This behavioral design pattern, neatly organize method usage across classes, it is An algorithm that can be changed at runtime.

you can follow this implementation in this video.
MVC Design Pattern: its stands for Model View Controller -Model: the object containing data
– View: the User Interface
-Controller: the middleman who handles the interaction between the model and view(handles all functionality)
This is the second part of desing patterns, but this time we are going to talk about some some Structural Patterns:
Adapter Design Pattern: This Structural pattern is responsable for matching interfaces between different classes , in other words it adapts incopatible and make it compatible and working together.

As you can see in the UML diagram above the interface WisardAdapter works as adapter for the fighter interface and the wizard class, you can see an very detailed implemented explanation in this video.
Bridge Design Pattern: in this design pattern You’re decoupling the abstraction from the implementation. You can progressively add functionality without affecting the others. You can see this in the UML example below

A good word to define this process could be split but without afecting. I hightly recomend this very good explained implementation of this design pattern by Derek Banas in this video.
Decorator Design Pattern: There’s a base class and you can use another class to layer on top of it on runtime.

you also can see its implementation in this video.
Facade Design Pattern: This structural pattern hides the inner workings, only shows you what you need to know/result. The facade object calls and manages all the processes that are needed to perform a task

As you can see in the UML diagram, facade design pattern uses the principle of abstraction, you can see its implementation here.
Design patterns are highly recomended to learn when we are trying to solve a software design problems in a very organized and efficient way. There are three types of desing patters but in this post we are going to focus in some creational patterns:
Abstract Factory Design Pattern: This design patthern is knowns as a class that handle the creation of abstract factory class where everything is encapsulate, in this design every step is separate as an abstract class or interface which make it more flexible. You can see a representation of it in the UML diagram below.

If you want to know more about this pattern watch this video or see this website.
Builder Design Pattern: This creational design pattern as named it is a builder class that takes differents objects an push it all together in order to create a new object.

This UML above show how a different way to make a complex object with Builder Design patthern , this video show step by step the structure of the builder pattern
Factory Design Pattern: This Creational Design pattern has a factory class that handles the creations of objects for other classes you can see a brief example of this in the UML diagram below.
Prototype Design Pattern: It is the design pattern that allows you to create new objects or instances by cloning other intances or objects at run time.
If you want to try the implementation, follow this Dereck Banas’s video on youtube about prototype design pattern
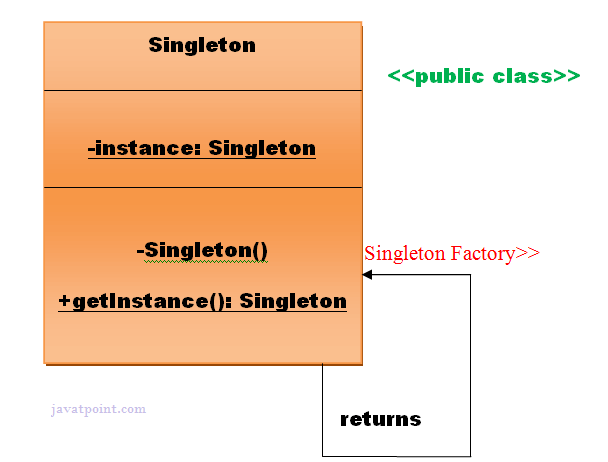
Singleton Design Pattern: This creational design pattern limit the creation of an object of a class to one. In a sigleton class the contructor is made private to make sure there is going to be a single instance of the class.
I have been told by mentors and professors that the better way to learn it is to teach it to try someone else. In this case I’ll teach you something cool that I learned and it called Strings Functions but this time in MySQL, for those who don’t know what that is , it is a database management system which stands for “My”, the name of co-founder Michael Widenius’s daughter, and “SQL”, the abbreviation for Structured Query Language.
Strings Functions are used mainly use for string manipulations which mean you can basically play with it , within he String Functions we can find few that are very important like ASCII(),CONCAT(),LENGTH(),UPPER() and SUBSTR().
ASCII(str) is it a function that returns the ASCII value of the String in the parameter for example :
SELECT ASCII('A') FROM DUAL;If we run this code the return value will be a column with the ascii value of string “A” which is is 65.

CONCAT(Str1,Str2) it is a function that returns a string which is the result of concatenating two or more arguments for example:
SELECT CONCAT('Life ','is ','beautiful ') from DUAL;
LENGTH(Str) this function will return the length of the given string for example:
SELECT LENGTH("Zawardo");
Upper(Str) this function will convert all characters within the given string to uppercase characters and then will return it for example:
SELECT UPPER("life");
SUBSTR(Str,Pos,Len) This function will return a specific number of character from a specific position of the given string for example:
SELECT SUBSTR("Beautiful",4,6);
These functions are very important when we want to add any change to our strings and these are not the only String functions that exits, there are few more and you can learn more about it here.